We all know that the Earth and the Moon attract each other due to their gravitational forces. Because of Earth’s larger size, its gravitational pull is mostly applicable on the moon. If Earth is pulling the Moon towards itself, logically the Moon should fall onto Earth, but that doesn’t happen, and it won’t happen in the future either. Why?
Why Moon Not Fell into Earth?
Put simply, the reason lies in the Moon’s revolution. The Moon orbits around the Earth, influenced by gravitational force. One might wonder why the Moon doesn’t stop or why it continues to orbit. Let’s understand.
We’re familiar with Newton’s First Law of Motion, which states that An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. This concept applies to the Moon as well. Due to Earth’s gravitational pull on the Moon, the Moon is unable to escape and move away from Earth in a straight line.
Due to orbiting the Earth, centrifugal force acts on the Moon. This keeps the Moon’s tendency to move away from Earth, but due to Earth’s gravity, it cannot do so.
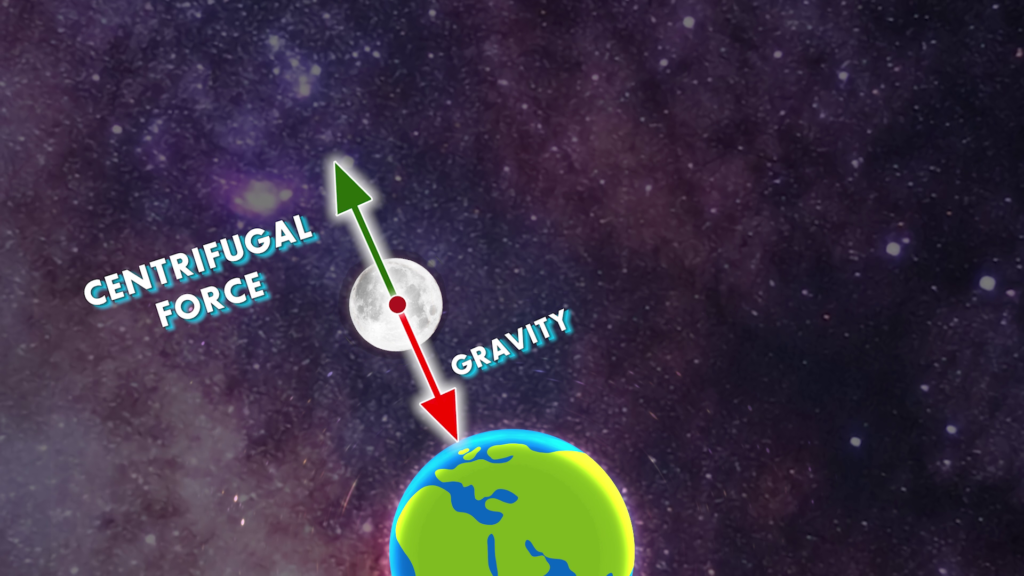
Let’s Understand With an Example
We can understand this by imagining tying a stone to a rope and swinging it in a circular path. The rope exerts a force towards the center of the circular path, known as centripetal force. This force is necessary to keep the stone moving in a circular motion rather than flying off in a straight line. At the same time, the stone experiences an apparent outward force away from the center of the circular path, known as centrifugal force. This force is a result of inertia, as the stone wants to continue moving in a straight line tangent to the circle. When you swing the stone at a constant speed in a circular path, the centripetal force exerted by the rope balances the centrifugal force experienced by the stone. This balance allows the stone to continue moving in a stable circular orbit. The rope experiences tension due to the force required to keep the stone moving in its circular path. This tension is what provides the centripetal force. On the Moon, Earth’s gravity applies, which functions as a centripetal force.
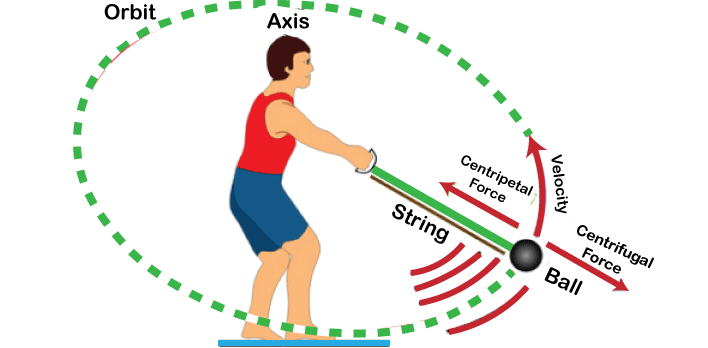
Why do Satellites Revolve around Earth?
The Moon is a natural satellite, and of course, it continuously orbits around the Earth, which is correct. However, do you know that when artificial satellites are placed in orbit, they are given a specific velocity so that their gravitational pull and centrifugal force become equal? This ensures that without any fuel, the artificial satellite will orbit Earth indefinitely.
Now, the question arises: who gave the Moon its velocity? The answer lies in the mystery of the Moon’s origin. There are various hypotheses about the Moon’s formation, but according to the latest research, the Giant Impact theory is considered the most valid.

Approximately 4.5 billion years ago, when Earth was still a fiery mass, it collided with a planet roughly the size of Mars. The impact was so powerful that it ejected debris from Earth into space. This debris eventually formed the Moon. The debris was ejected with such perfect velocity and angle that the resulting gravitational pull and centrifugal force became equal, allowing the Moon to begin its orbit around Earth.
Orbital Velocity Explained
Now, let’s talk about orbital velocity. The Moon orbits around the Earth, which is good. But if, for some reason, the Moon were to suddenly stop, would it stay in its place? No, it would fall towards Earth.
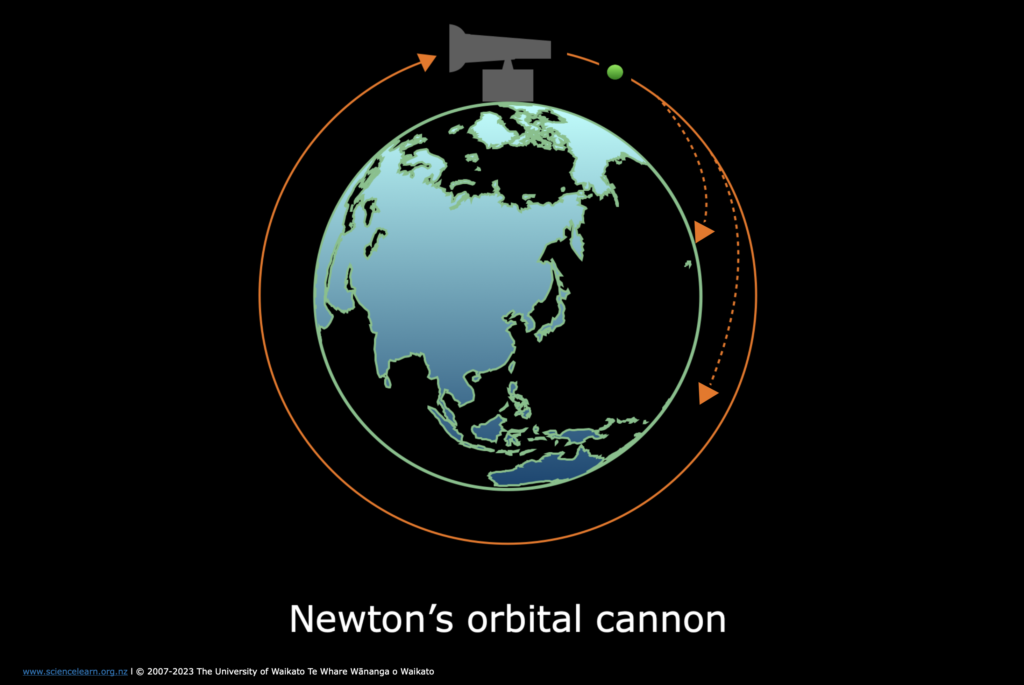
For the Moon to remain in its position, it requires a forward velocity. When Newton first discovered gravity in the 17th century, he also pondered over why two celestial bodies orbit each other. It took him 20 years to find an answer through a thought experiment called “Newton’s cannonball.”
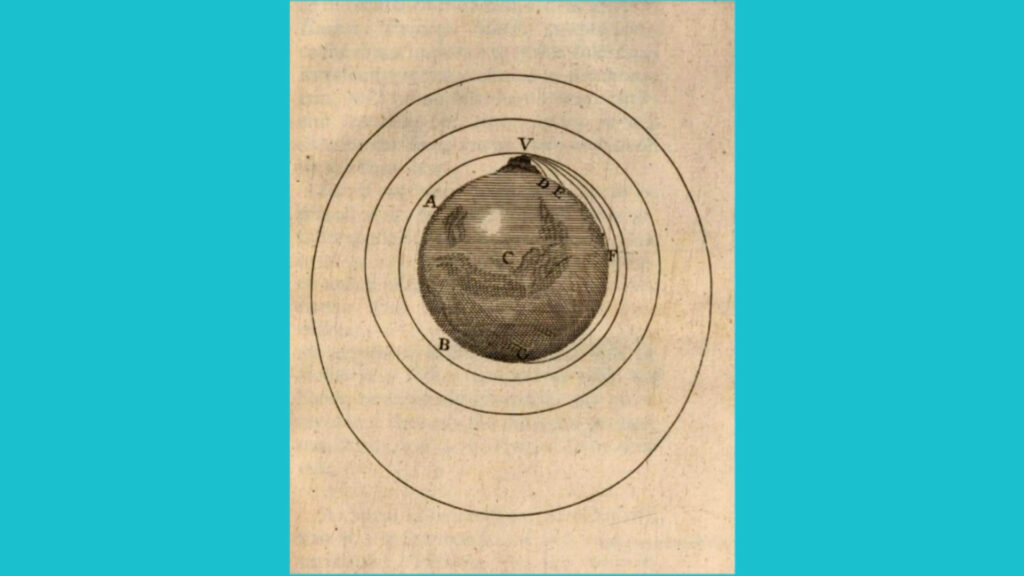
In this thought experiment, imagine standing on a gigantic mountain with a powerful cannon aimed at the sky. The cannon is powerful enough to launch a cannonball into space, giving it escape velocity and sending it toward the Moon.
Now, imagine that the force of the cannon is adjustable. Initially, when fired with minimal force, the cannonball falls a short distance away. Gradually increasing the force, the cannonball travels further until it eventually completes a full orbit around Earth. If the cannon were not there, the cannonball would continue orbiting, demonstrating that it had achieved orbital velocity. The gravity and centrifugal force acting on the cannonball would be equal. So, friends, this is the reason why the Moon doesn’t fall onto Earth.

Loved the last part of the explanation!!