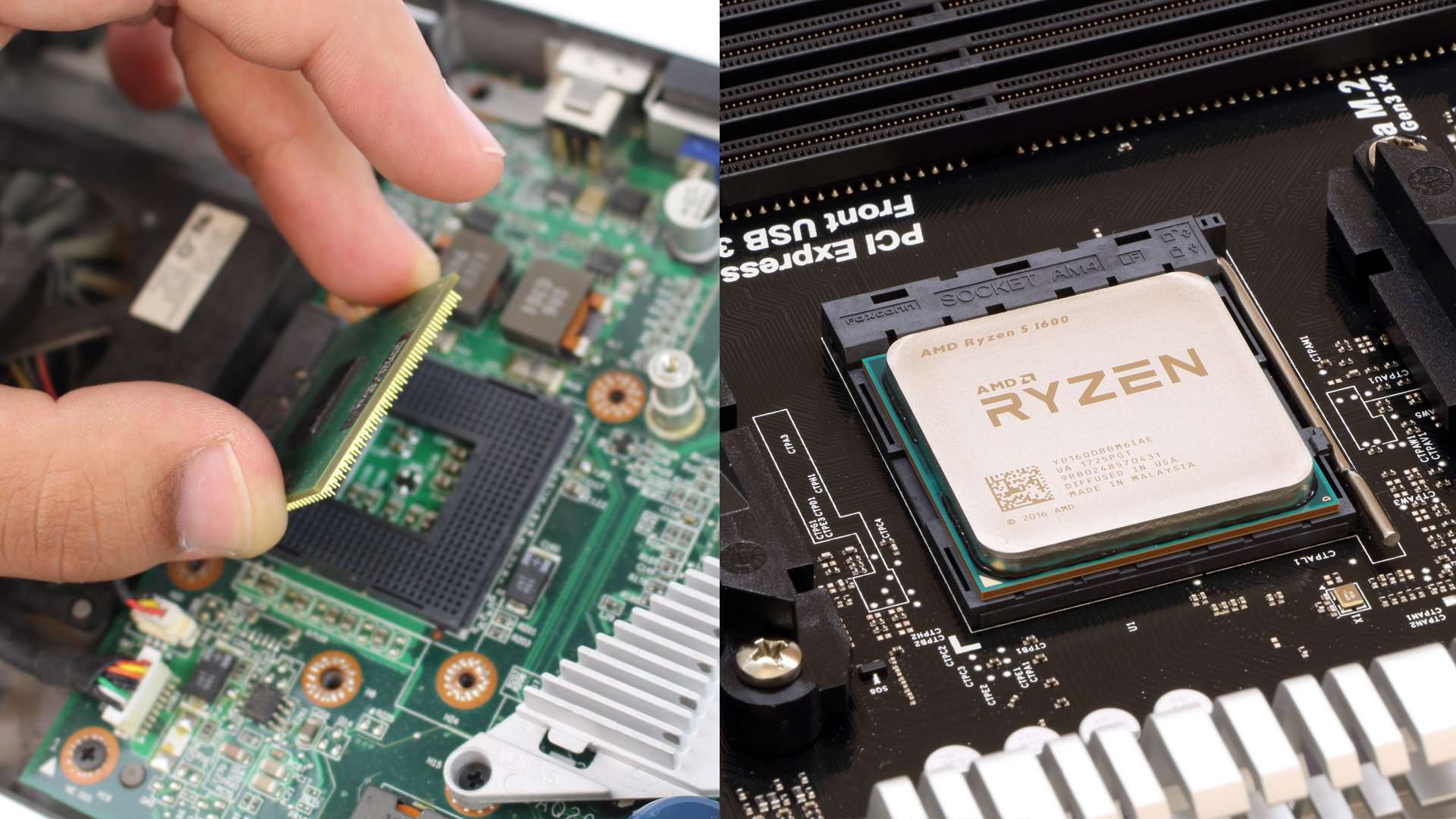
CPU AKA Processor is a silicon-based component that is a very essential part of every single type of computer. But they are obviously not interchangeable with each other. A smartphone or a tablet possesses a different type of processor while a laptop has different, a server has a different one & a desktop too. There Architecture, Core count, frequency, socket are completely different & also sometimes, CPUs are detachable from the motherboard & sometimes not. In this article, we’re not bothering you much about server and smartphone CPUs, here we are only dealing with the differences of Laptop Vs Desktop CPU. You may get shocked to know that not only the CPU but every single component of a laptop is different from than desktop! You may ask why? Here are the answers for you.
Read More: 2.5 Vs 3.5 HDD: What is Better & Why?
Laptop Vs Desktop: Form factor
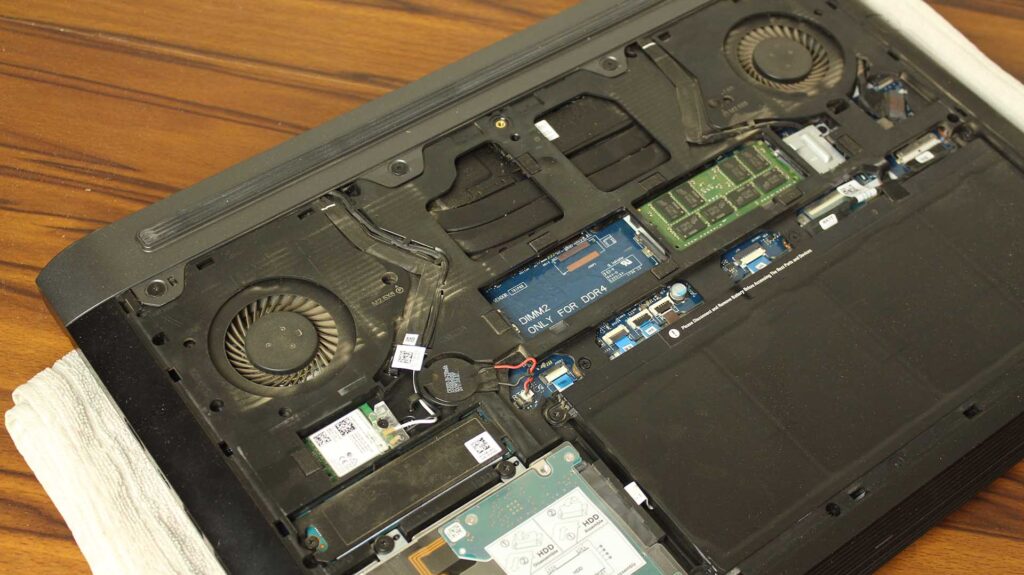
As it is said, laptops are designed to keep the limited space in mind which is why every single component of a laptop is way smaller than a desktop’s – GPU, RAM, HDD, Motherboard Board, & even the fans. Because of this small design, laptops are definitely portable and take less space on the tabletop. This small form factor also creates many problems that even the manufacturer’s engineers can’t control much which we will discuss in a while.

On the other hand, desktop machines have no limited space. You as an end-user, can increase or decrease the form factor of your computer according to your needs. You can build smaller desktop PCs with micro – ATX or mini ITX motherboards or just can pick full form factor ATX motherboard which is totally up to you. Either you’re building your gaming PC or editing your PC or, just a simple computer to carry on day-to-day tasks. In all cases, you have that option.
In terms of laptop gaming, yeah! It looks cool, consumes less space on the tabletop, is portable but unfortunately, that’s why laptops are underpowered than desktops!

Is there any performance difference between Laptop Vs Desktop CPU?
The answer is yes, Desktop CPUs are much more powerful than laptops. Let’s take an example, If a desktop is assembled with Intel Core i7 7700 CPU, GTX 1060 6GB Graphics Card, 16GB of RAM, 256 GB of SSD and a laptop is built with Intel Core i7 7700HQ CPU, GTX 1060 6GB (Mobile) Graphics Card, 16GB of RAM, 256 GB of SSD then no doubt desktop is the winner in this case. If you invest for example 800$ on a gaming PC and the same 800$ on a gaming laptop then of course you get much more performance on the desktop than a laptop. Their price-to-performance ratio is lower than the desktops.

When laptop CPUs are designed, their primary concern is the power usage than the performance because laptops are not always plugged in onto the wall outlet. So, when it is running from the battery then it should not drain the battery in a couple of minutes that’s why their performance is minimized than a desktop CPU.
I don’t know whether you have seen it or not, the laptop’s performance is extremely decreased when it is running from the battery. This time the CPU underclocks itself to reduce the power usage.

How Can I forget about Heat?
As laptops are so compact by design, there are definitely not much head rooms for a good and efficient cooling system. We can’t fit 5 or 6 fans inside the laptop chassis as we do on the desktop. laptop fans are so small and there is not much space to fit multiple ones so think it if a laptop outputs performance like desktop then it produces almost similar heat which can’t be taken out from the laptop and its components will be degraded over time and also the user can’t experience that smooth performance too. As CPUs and other PC components are heated up, they all have a fail-safe circuit that protects them to be destroyed by overheating.

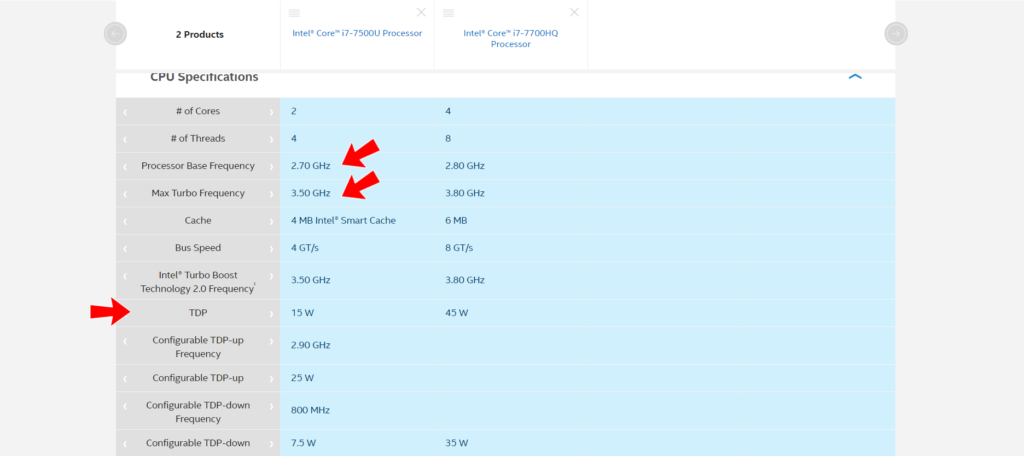
Now you can relate why the TDP value of laptop CPUs is always lower than desktops’. Take the picture below as an example.

TDP – Thermal Design Power rating which indicates the maximum amount of heat that a processor can generate. TDP rating measures in Watts. A laptop processor comes with lower TDP ratings, in comparison to a desktop processor.
Laptop Vs Desktop CPU: Number of Cores and Operating Frequency
In both cases, desktop CPUs are the winner. They possess more core count and more clock speed AKA frequency. As core count increases and clock speed increases, the CPU gets more and more powerful but it also produces more heat. That’s why slim profile, power-efficient laptops have Intel ‘U’ or ‘Y’ series CPU. These are specifically designed for power-efficient devices. If you compare the core count and frequency with the desktop counterpart, you will find huge differences. For example, Intel Core i7 7700 and Intel Core i7 7500U. Notice the differences in the image below.
Though there are some laptop CPUs available in which the output is pretty good such as Intel ‘H’ series (ex. Intel Core i7 7700HQ) but nowhere close to desktop. Notice the differences in the image below.
Are Laptop and Desktop CPUs interchangeable?
Most probably, no. Laptop CPUs are completely different. Most of the time, they are soldered on the laptop’s motherboard and if they’re not, desktop CPUs can’t be placed on their sockets. In most cases, for those laptops which consist of Intel CPUs, use PGA sockets – Pins are mounted on the CPU.

On the other hand, Intel desktop CPUs use LGA sockets. And if you’re thinking that in the place of Intel processor-based laptop’s PGA socket, you can insert AMD CPU then it is not possible as the socket probably doesn’t match if somehow it matches then the CPU will not work for sure.
Read More: CPU Sockets Explained! LGA Vs PGA Vs BGA
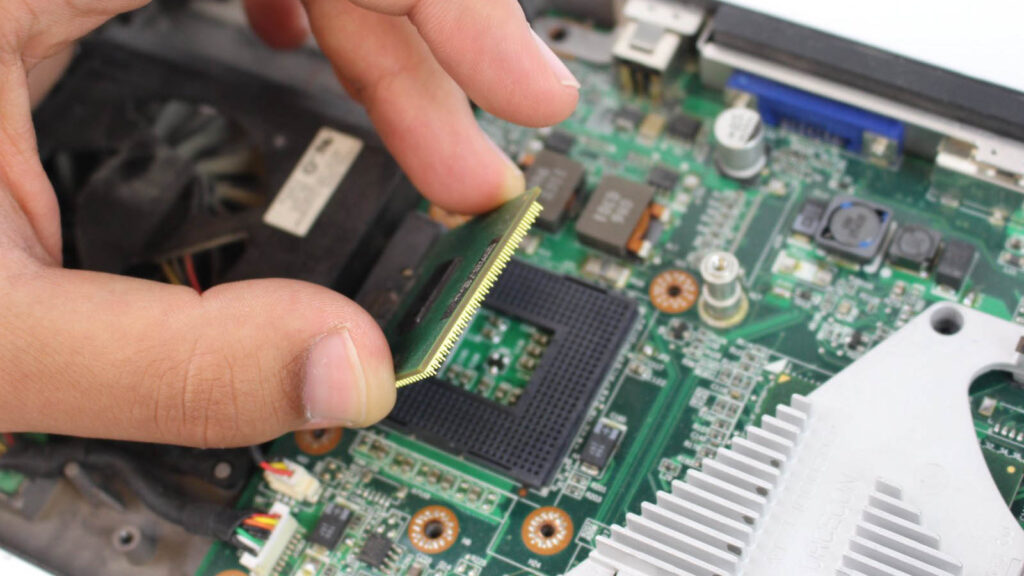
How to Replace Laptop CPU?
Changing laptop CPU is kind of a garbage idea for most of the time. As I earlier said that laptop CPUs are generally soldered on the motherboard if it possesses a socket system then it is very hard to find that CPU you’re currently using if you want to upgrade it with a bit powerful one then it is much harder to find that. And if you will get it then it may not work.
In terms of desktop, however, it’s very easy to replace CPU in the same generation like if you already have Intel 6th gen i3 then you can upgrade it with 6th gen i7.

If the motherboard you’re using supports multiple generations like X370, A320, B450, etc. then you have lots of upgradation options. For example, if you have purchased Ryzen 3 1200 3 years ago then you can replace it with Ryzen 7 3700X easily (if you have purchased X370 motherboard).

If you’re reckless and want to invest in a new motherboard then you have lots of options to choose from. You can’t do that on a laptop obviously. Its components are not replaceable like this.
Read More: Chromebook Vs Laptop: Which One Should You Pick?
In the Concluding Lines…
Frankly, I never recommend laptops to designers, content creators, and gamers but if you travel a lot or you have not much space in your home or office to set up a desktop then you can go for a laptop otherwise always a desktop is recommended. If you’re a student and need a computer for your study then from my side, always a desktop is recommended. Desktops provide much more price to performance value to the users. Therefore, I hope that you have really understood this article about Laptop Vs Desktop CPU. If it really so then don’t hesitate to express your valuable thoughts in the comment section below. Thanks for visiting & appreciating our work.