RAM modules stand as vital components within your PC, offering a plethora of advantages, from significant performance enhancements to the ability to handle multitasking seamlessly. Understanding the how to choose best RAM for your PC and laptop preventing unnecessary expenditures. Here’s a guide on making informed RAM choices while optimizing your spending.
Choosing RAM Configuration: Dual Channel vs. Single Channel
One fundamental aspect to choose the best RAM for a PC and laptop is whether to utilize your RAM in single-channel or dual-channel configuration. Avoid using RAM in single-channel mode for optimal performance. For instance, if you intend to install 8GB RAM, place two 4GB sticks in either the 1st and 3rd slots or the 2nd and 4th slots. Similarly, for 16GB RAM, opt for two 8GB sticks, and for 32GB, choose at least two 16GB sticks.
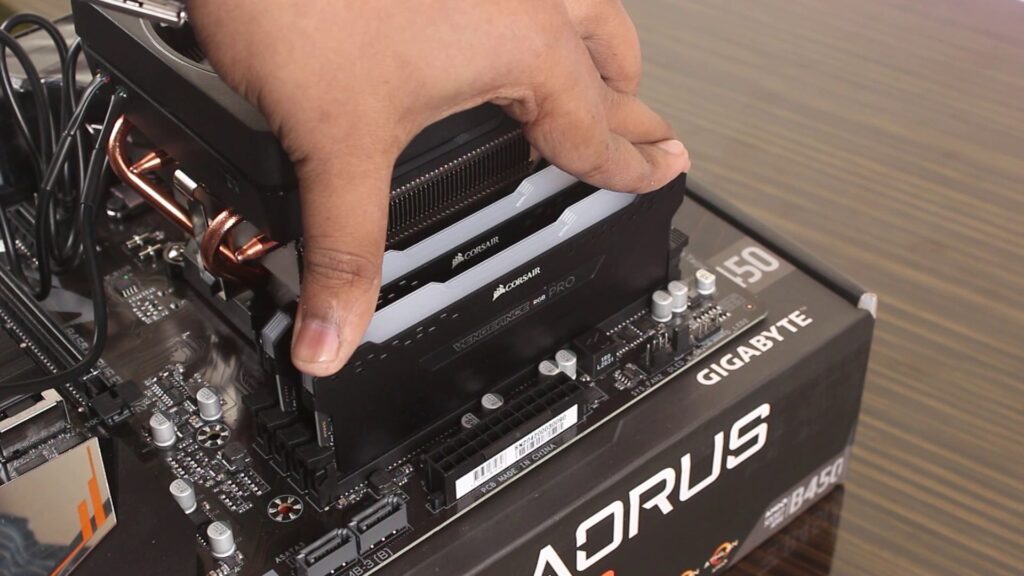

In cases where your motherboard accommodates only two RAM slots, you can still achieve a dual-channel configuration by using both slots. This method offers improved transfer speed and bandwidth, enabling your system to handle information more efficiently. This, in turn, enhances your system’s overall performance, particularly during memory-intensive tasks like video editing. Notably, if you’re using on-board graphics, a dual channel configuration can significantly enhance performance. Moreover, the cost difference between two RAM sticks and a single stick of the same capacity is usually negligible, making the choice even more practical. This strategic RAM selection process encapsulates the essence of how to choose the best RAM for PC and laptop systems, ensuring an elevated computing experience.
Understanding Memory Timing and CAS Latency
When purchasing RAM, people often focus on capacity and frequency, but memory timing is equally crucial. However, this aspect is often overlooked. One essential parameter to understand is CAS latency (CL), denoted by the “CL” value. A lower CAS latency is better, as it indicates faster data access. When you see a lower CL value, it signifies that the RAM can retrieve data more quickly, leading to improved overall performance. By integrating these factors, you can effectively navigate the process of choosing optimal RAM for your PC and laptop, ensuring an efficient and effective computing experience.

Not always CL is mentioned sometimes it is presented as a sequence of numbers, like 9-9-9-24 or 5-5-5-15, on the RAM’s specifications. However, the most commonly emphasized figure in this context is the CAS latency (CL). The first number like ‘9’ in the first sequence and ‘5’ in the second sequence and CAS latency represents the delay between receiving a command and the RAM’s ability to provide the requested data, measured in clock cycles. For instance, if a RAM module specifies a CL of 9, it signifies that the RAM requires nine clock cycles to furnish the requested data after the initial command. Similarly, a CL of 15 implies a fifteen-clock-cycle delay. In this context, a lower value is preferable, as it indicates quicker data delivery.
CAS Latency in Nano Seconds
Currently, these values are not in seconds, so we need to convert them. With this formula (CAS Latency/RAM Speed)*2000). The answer will be in nanoseconds, essentially. Now just notice the result will be influenced by the RAM frequency. So, as you can understand, latency and frequency work together.

Let’s take an example: DDR4 with 1866 MHz and CAS latency of 13, and DDR4 with 2400 MHz and CAS latency of 17. Now, let’s determine which one is faster. 1866 MHz faster because its latency is lower compared to 2400 MHz.

In simpler terms, you can think of memory timings are the response time of RAM. The lower the timing, the more noticeable its impact on your daily tasks, especially in activities like multitasking and gaming. Higher clock speed doesn’t always provide an advantage; higher clock speed is beneficial for massive software that involves heavy data transfer such as Adobe Premier Pro and Adobe After Effects, Blender, etc. If you aim for a good balance then aim for both parameters – CAS Latency and Frequency.
RAM Clock Speed: Measuring Performance in Megahertz
RAM performance is influenced by factors like clock speed and capacity. Clock speed measures RAM in megahertz (MHz), denoting the number of data cycles the RAM can handle in a second. For instance, 1 megahertz represents 1 million cycles per second. Calculating this, we can determine that 3000 megahertz equals a certain number of cycles. A higher frequency indicates faster data transfer rates and, consequently, greater bandwidth. This knowledge forms the foundation for making informed choices when considering the best RAM for your PC and laptop.
Clock Speed’s Role: Higher isn’t Always Better
Clock speed is a gauge of how much data RAM can send and receive per second. However, it’s crucial to consider latency as well to grasp the true speed of RAM. It’s essential to consider both aspects to accurately assess the RAM’s speed. It’s important to note that purchasing a 6000 megahertz DDR5 RAM doesn’t guarantee super-fast performance. If the processor or graphics card isn’t equally capable, the system’s performance will be bottlenecked by these components. Moreover, the RAM slot type is significant: DDR4 slots only support DDR4 RAM, DDR3 slots only support DDR3 RAM, and similarly, DDR5 slots support DDR5 RAM. These are not interchangeable. So, choose RAM for your laptop and PC with this in mind.
Don’t Miss: Can You Use 4GB And 8GB RAM Together?!
Budget Allocation on Different Components
It’s wise to purchase RAM sticks in accordance with your budget. As I have mentioned multiple times, a practical approach is to allocate 40% of your budget for the graphics card, 25% for the CPU, and the remainder for the motherboard, RAM, cabinet, fans, power supply (SMPS), and other components. This ensures a balanced distribution of resources and helps you make informed choices aligned with your computing needs.

Choose RAM Capacity and Frequency Wisely
For an average user engaged in activities like browsing, music streaming, movie watching, and using software like Word and Excel, 8 gigabytes of RAM is more than sufficient. If you’re aiming for a slightly more high-performance, then installing 16 GB of RAM is recommended. For users who tend to open multiple browser tabs, run various programs simultaneously, and extensively use video and audio editing software, 32 gigabytes of RAM should be ample. Going beyond this capacity is generally unnecessary. Utilizing a dual-channel configuration by installing two 16 GB sticks is a practical approach for 32 GB of RAM. When it comes to frequency, 3200 megahertz is often more than enough for most tasks. This selection process guides you toward the ideal RAM choice, ensuring optimal performance for your PC or laptop.

Heat Sinks on RAM Modules: Are They Necessary?
A prevalent trend nowadays is the attachment of heat sinks to RAM sticks. Some higher-priced RAM modules come equipped with these features. But do RAM modules genuinely require heat sinks? The answer is both yes, if you plan to heavily overclock your RAM. However, for the typical casual user or even a heavy user who isn’t engaging in extensive overclocking, heat sinks aren’t necessary.

If you’re looking to save money and you’ve found a RAM stick without a heat sink at a lower price and offered by a well-known brand, feel free to go for it. It won’t impact performance. A RAM module without a heat sink will perform just as well as one with a heat sink, provided that it’s from a reputable brand, offers good frequency, low latency, and suitable capacity, and is accompanied by proper warranties.
Also Read: RAM or SSD Upgrade – Which Boosts Max Laptop Performance
RAM modules usually don’t encounter significant heating issues. So, spending extra money solely for heat sinks isn’t necessary. However, if aesthetics matter to you, then you might consider opting for RAM with heat sinks. These heat sinks not only enhance the visual appeal but also provide some cooling benefits. If RGB lighting is your preference, then heat sinks become almost essential as they often encase RGB lighting components. Sometimes the heatsinks or casing of the RAM are made out of plastic which is nothing to do with heat transfer it’s only for aesthetics and if the RAM supports RGB then this plastic enclosure holds the RGB components.

In conclusion, while the choice of RAM with or without heat sinks is mostly based on personal preferences and specific use cases, practical performance gains can often be achieved without the need for elaborate heat sink designs. The decision should align with your budget, needs, and desire for aesthetics.
Conclusion
So, if you are planning to choose the right RAM for your PC or laptop, it frankly involves so many things. You need to understand dual channel vs. single channel configuration and understand memory timing, particularly CAS latency, have an idea what is the right capacity RAM for you and what would be the sweet frequency for you. These factors collectively impact how well your system performs, making informed choices essential for optimizing your computing experience. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that you’re making the most of your computer’s capabilities and enjoying a seamless user experience.
