Nowadays, USB-C is everywhere from our smartphones to laptops, and notebooks, and in each and every portable device. USB-C came out on 2014. The original version of USB aka USB-A is not gone anywhere. USB-A is still fully in use but if we compare USB-A and USB-C then there are many noticeable differences. In this article, we are going to compare them and find out those conditions in which USB-C is better and where USB-A can’t be dominated
What is USB Type A Port?
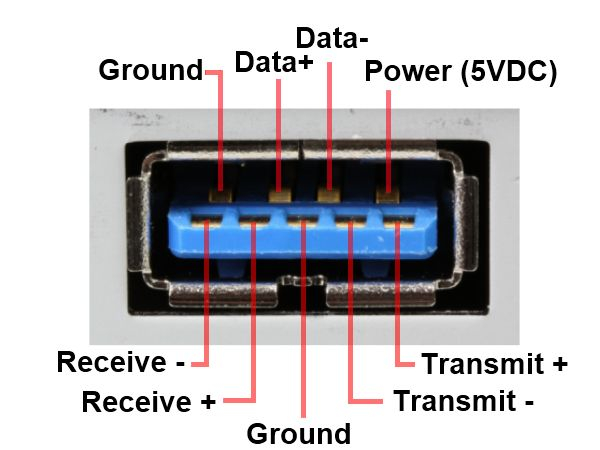
USB-type A was introduced with the original version of USB 1.0 back in 1996. USB-type A can easily be identified by its rectangular nonreversible design. USB-A port is everywhere still now. In most laptops, smart TVs, video game consoles, DVD players, and even in home theatres. Still, many storage devices can only be possible to connect with USB-A ports. After so many years, the glory of the USB-A Port has not faded anymore. However, the specs of the USB-A port are not as same as in the ’90s. The speed and features are highly revised.

USB Different Versions Explained:
USB 1.0 has a maximum speed of 1.5 Mb/s (megabits per second) with 2.5 watts of power delivery. USB 1.1 though which was introduced back in 1998 the speed is slightly improved and can reach up to 12.5 Mb/s (megabits per second). In the year 2000, everything changed with the introduction of USB 2.0. The speed is boosted to 480Mb/s (megabits per second) with the exactly same 2.5-watt power delivery.

As time progresses the speed of USB 2.0 is failing to satisfy enough. In the year 2008 engineers developed the new version – USB 3.0 with up to 5Gb/s (gigabits per second) of transfer speed and 4.5 watts of power delivery capability. The speed is again revised with USB 3.1 in 2013 at 10Gb/s (gigabits per second) of transfer speed. The next revision USB 3.2, only supports USB-C. However, after the release of USB 3.2 USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 are renamed and are now known as USB 3.2 gen 1 and USB 3.2 gen2 respectively. Every generation of USBs is fully forward-backward comfortable. Depending upon the version manufacturers used different color codes you can check Our article on USB Ports Color Code Explained – Each Color Tells Something!

What is USB-C?
USB-C was introduced with USB 3.1 back in 2013 – 2014. A revolutionary connector that is not only in use with USB but also supports so many different interfaces which are known as USB-C Alternate Modes. With USB-C, manufacturers can design the devices much slimmer, and as this one port can do multiple things so the necessity of having a different port for different interfaces will be reduced. Okay now, let’s discuss the differences between USB-A and USB-C.
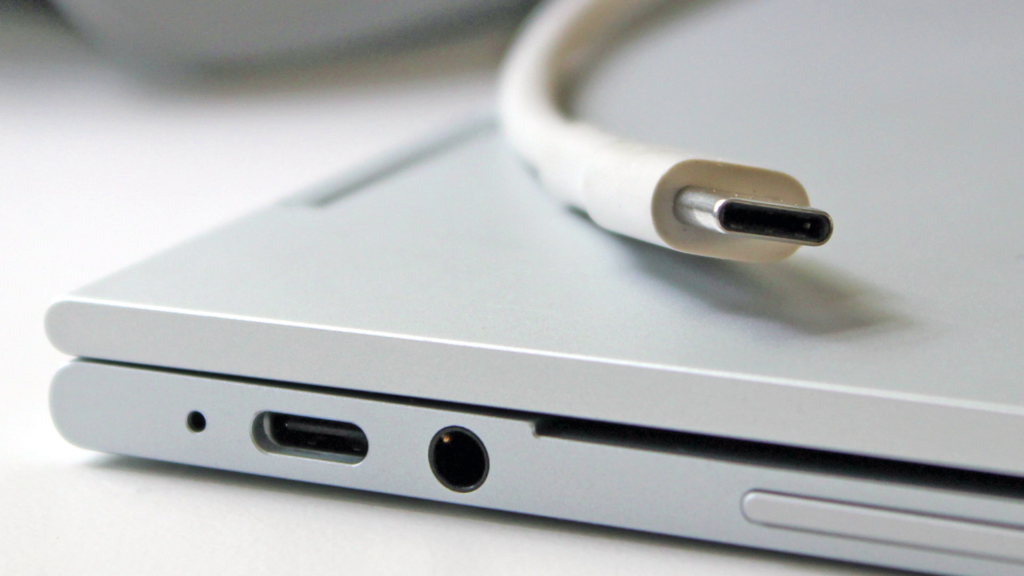

USB A Vs USB C
USB A is definitely quite bulky and not that much sturdy. Because of the size shape and design limitation, the speed of the interface can’t be improved after USB 3.1 – 10Gb/s version. The pin limitation of USB A also blocks to use of different alternate modes like USB C. Anyway let’s understand the differences between USB A and USB C.
USB C is Slim & Reversible
Just as USB-C visually appears slimmer and thinner but the advantage on top of this is its reversibility. How is that possible? that’s possible due to symmetrical pin placement on both the bottom and top of the USB connector.

USB A, on the other hand, is currently now standardized so its design can’t be changed. All the pins of USB A are placed on the bottom side of the port.

USB C Port has Lots of Pins
The greatest advantage of having extra pins is that using those pins it is possible to increase the speed and the functionality of the interface. That’s why USB 3.2 and USB 4.0 is only limited on to the USB C.
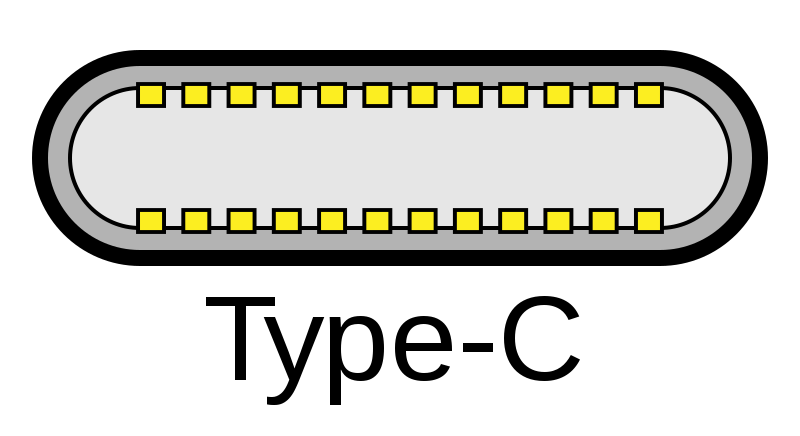
Those extra pins also help with power delivery and other Alternate Modes. USB-C has a total pin count of 12 on a single side. Combining both sides it is 24 Pins. This is the diagram.

USB C Power Delivery
USB C can deliver up to 100 watts of power. This is definitely not possible with USB A. However not all USB-C ports and USB-C cables are capable of this. If a brand wants then they could add this feature to charge the device itself or to power another device via USB-C.

Just think of it, you have a laptop with a USB-C port. That USB-C port supports the ‘Display Port’ Alternate Mode and can handle 100W of power. With the right USB-C to USB-C cable, you can power and transfer the display signal to a monitor. How cool is that? Even if the monitor is plugged into a wall outlet and can output sufficient power over USB-C then your laptop will be charged with only that USB-C port. These advantages can’t possible to get with USB-A. Now USB-C can handle up to 240W of power – of course with the right cable, right adapter, and right device.
USB C Backward Compatible
Sound strange but it’s the fact. In USB C any USB revision can be used. I mean USB-C ports can be USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, and even USB 4.0.

For instance, your laptop with a USB-C port that supports USB 4.0 can run USB 2.0 devices either with their connector conversion (USB-C to USB-A converter) or directly with USB-C Cable. Until the device you are plugging in with your laptop support USB 4.0 standards, the USB-C port will work on the maximum supported protocol of the connected device. So it’s definitely backward compatible.

It is also forward-compatible. Think of it if the laptop you’re using has a USB-C port but can support USB 2.0 specification and the connected device support USB 3.1, USB 3.2, or even USB 4.0. Will it not work? Of course Work. That’s the magic of forward compatibility.
USB-C Alternate Modes are Amazing
USB-C has lots of different Alternet modes HDMI, Display Port Thunderbolt, and MHL. These alternate modes allow manufacturers to reduce the number of I/O ports which not only makes the device slim but also cost-effective. However not all the Type C port support all of these alternate modes. It is up to the manufacturer what they want to provide. To use the alternate modes if it support all you need is just a suitable adaptor or cable depending upon your need. As I have mentioned before USB type A can’t have any of these alternate modes.
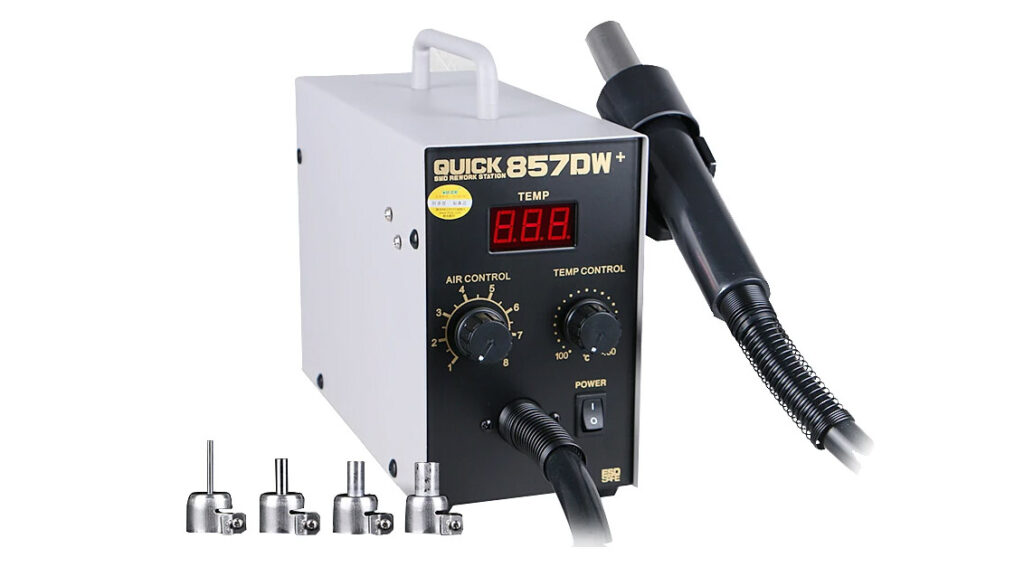
Hard To Repair
USB-C ports can’t easily be repaired. To replace a USB-C port you need special equipment like hot air soldering station, proper soldering paste, etc. On the other hand, to replace USB-A port you just need a soldering iron that’s it.

USB-C is Durable
USB-C port is much more durable than each and every connector that has been released until now. USB-C connector can allow plug-in and plug-out up to 20000 times. Way higher than USB-A only capable of 1500 times to 10000 times on paper.
In the Concluding Lines…
USB A and USB C are both great from their own perspective. I am not defaming any one of them. I am just telling you the advantage that USB-C can offer but USB-A can’t. USB A is still the king of the market because it is hard to find any device without USB A. I hope you guys understand the differences between USB-A and USB-C. That being said hope you guys have enjoyed this article and learned something new. If so then don’t forget to express your thoughts in the comments below. Thanks for visiting.
