Nowadays Type-C ports are commonly used in so many devices. From Macs to Windows machines, smartphones and even some of the other devices are now featuring this connector but all the Type-C ports are not the same. It’s up to the manufacturer which protocol or interface this connector supports.

Especially on laptops, a Type-C port’s capability is sometimes limited on USB, but some of them feature thunderbolt and some Displayport but for an average person it is really hard to identify which port support which Interface or protocol. If you’re one of them then don’t worry because, in this article, we will try to explain all the details so that you can identify the capabilities of a particular Type-C port on your own.
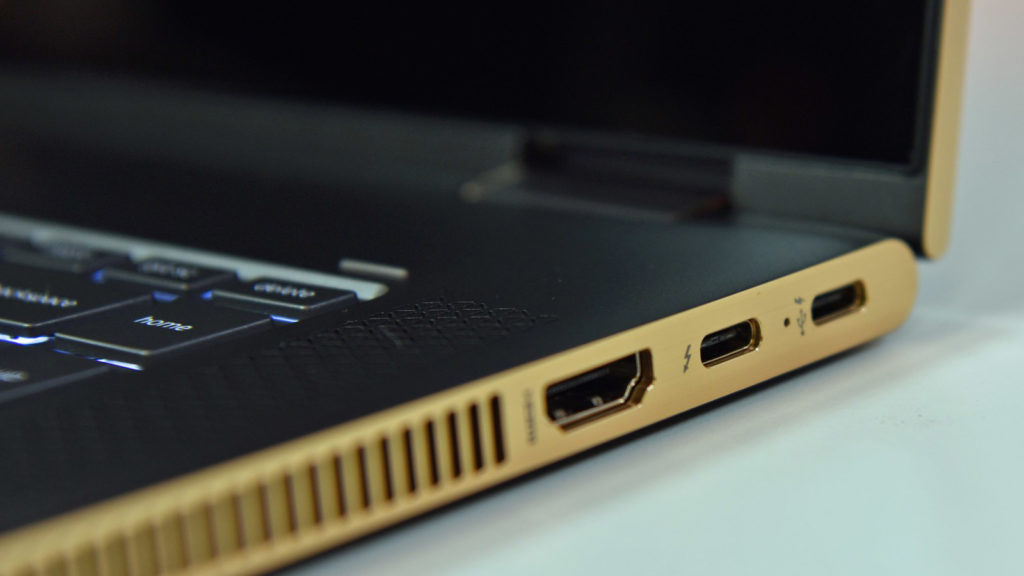

Basics of USB Type-C
USB-C is an industry-standard connector that was developed by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF). It was designed to carry data and power on a single cable. Though Type-C looks quite similar to micro USB, it isn’t. Over micro USB, it features a total of 24 pins whereas micro USB only has a total of 5. Because of its flip-ability, it has no up and down orientation like other connectors of USB.
Also, Type-C cable offers the same connector on both ends, so you don’t have to figure out which end goes where. That is not the case with the other USB cables we’ve used because most of the time, you have different connectors at each end. And finally, let’s know about durability. It can be plugged in or out more than 10000 times. So, if your phone has a Type-C port and you have plugged in and out your charger two times a day then the Type-C port can last 13 years which your device may not live long whereas a standard USB Type-A has a minimum rated lifetime of 1,500 cycles of insertion and removal, the mini-USB receptacle has only 5,000.
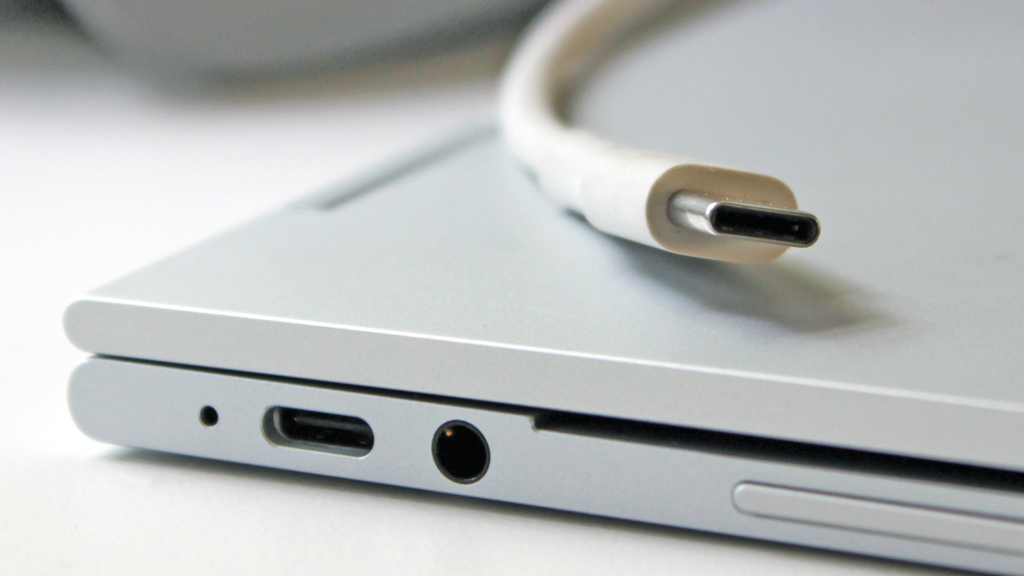

USB TYPE C Charging & Power Delivery Capabilities
USB Type-C was designed to deliver power and signal simultaneously and it was standardized to deliver up to 100W of power and the new revision of Type-C can deliver up to 240W of power at 48V rail 5A of current but that doesn’t mean that all the Type-C ports are designed for 100W or 240W of power delivery. It is completely upon the manufacturer who has designed that particular product. If a Type-C port is designed for any high amount of power delivery then it is obviously mentioned on the manual of that gadget.

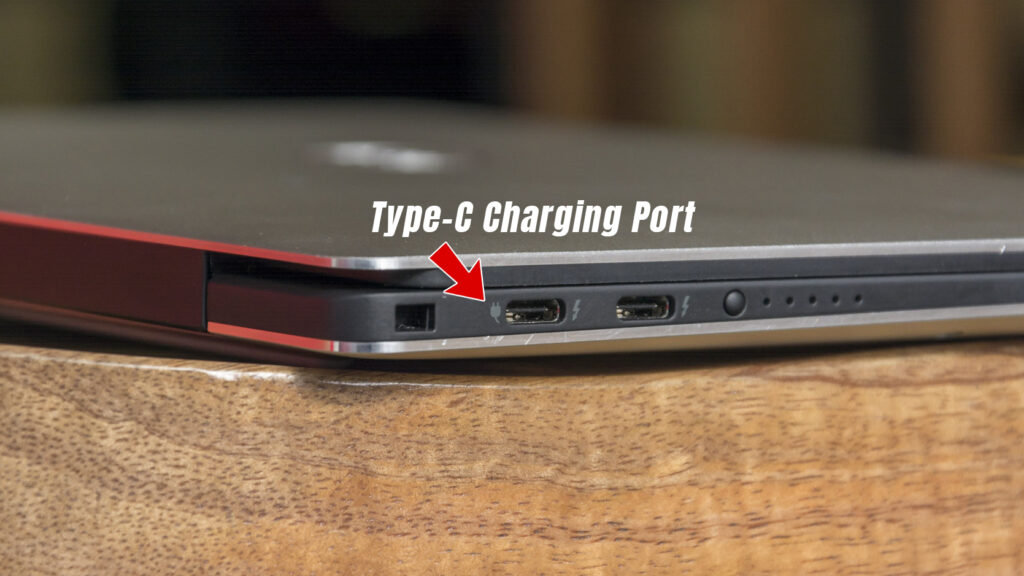
Sometimes, you have probably seen that laptops are charged by the Type-C ports. You can find a small logo (as shown in the image below) near the Type-C port and if a Type-C port is capable of power delivery then mostly a battery logo can be found anywhere beside the port.

All the Type-C ports support USB!
Yes, you heard right, all the type C ports all over the world support one of the USB standards. Maybe it’s USB 3.2 or USB 3.1 or USB 3.0 and even USB 2.0 but it’s guaranteed. Even graphic card’s Type-C ports have the support of at least USB 3.0 and maybe with different cards, it might go higher. If a Type-C port is capable of supporting DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, MHL, or HDMI then also it supports at least a basic feature of USB which is nowadays USB 2.0. Basically, Type-C was introduced with USB 3.1 which offers twice as fast as USB 3.0 (USB 3.0 theoretically supports 5Gb/s whereas USB 3.1 theoretically supports 10Gb/s).

USB Type-C Alternate Modes
There are several alternate modes are supported by USB Type-C. Vendors may support proprietary modes for use in dock solutions and keep in mind that Alternate Modes are optional.
In Type-C alternate modes, DisplayPort, Mobile High Definition Link (MHL), Thunderbolt, HDMI, and Virtual Link are included. Other protocols like Ethernet may have been included in the Type-C alternate modes in near future, although Thunderbolt 3 and are also capable of 10 Gigabit Ethernet networking.
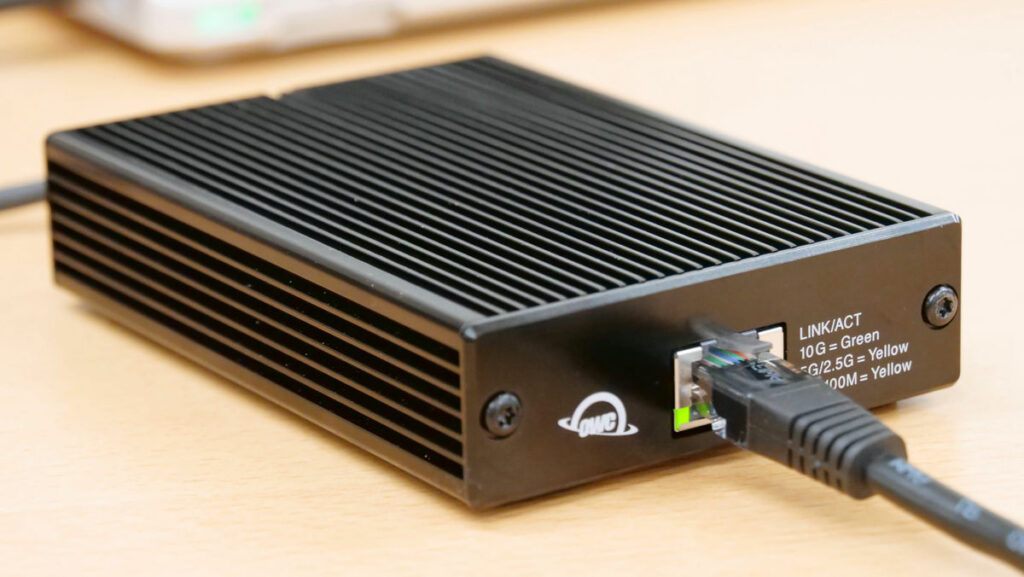

How to Identify a DisplayPort Over Type-C?
In various alternate modes of Type-C, DisplayPort alternate mode is commonly used in compact devices. As Type-C supports DisplayPort 1.4 and DisplayPort 2.0, there is no need for a bulky DisplayPort connector on the laptops. Also, the reversibility, durability, and power delivery capability make it unique. Mostly, those Type-C ports which support DisplayPort alternate modes have USB PD support that means if you connect a monitor with a Type-C port, the monitor takes power from this port along with the data signal. Keep in mind, the monitor should have the Type-C port and both the devices have to be connected with a Type-C to Type-C cable. If it is ‘Type-C full-featured cable’ then there is little chance of getting anything wrong.

Mostly, USB PD (USB Power Delivery) supports along with DisplayPort alternate mode over Type-C is commonly seen on the Type-C ports of the graphic cards and sometimes on the laptops. It is definitely better to check on the manual whether your laptop supports USB PD with DisplayPort or not.
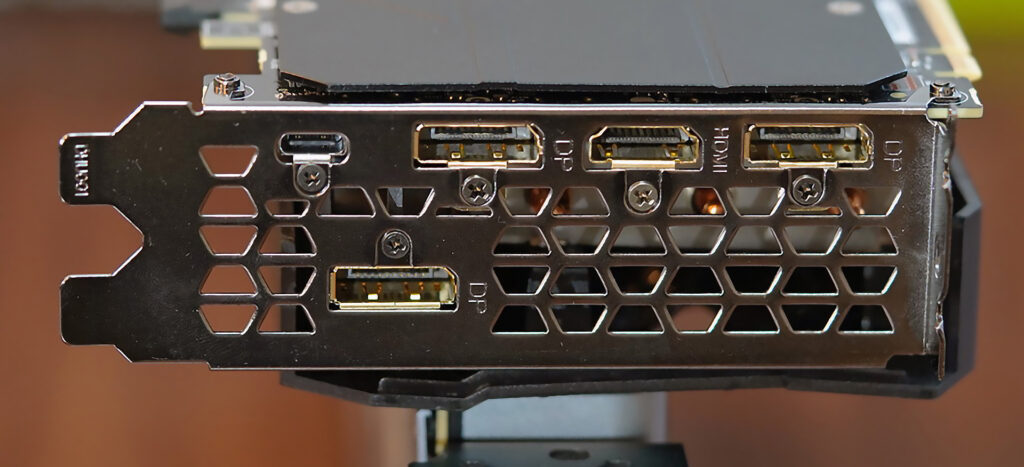

Mostly, those Type-C ports which support DisplayPort alternate mode have a small logo like shown in the picture below beside the port. It clearly indicates that the port has the DisplayPort capabilities but you can’t understand the DisplayPort version by just following the logo. You have to check the device specification for more details.
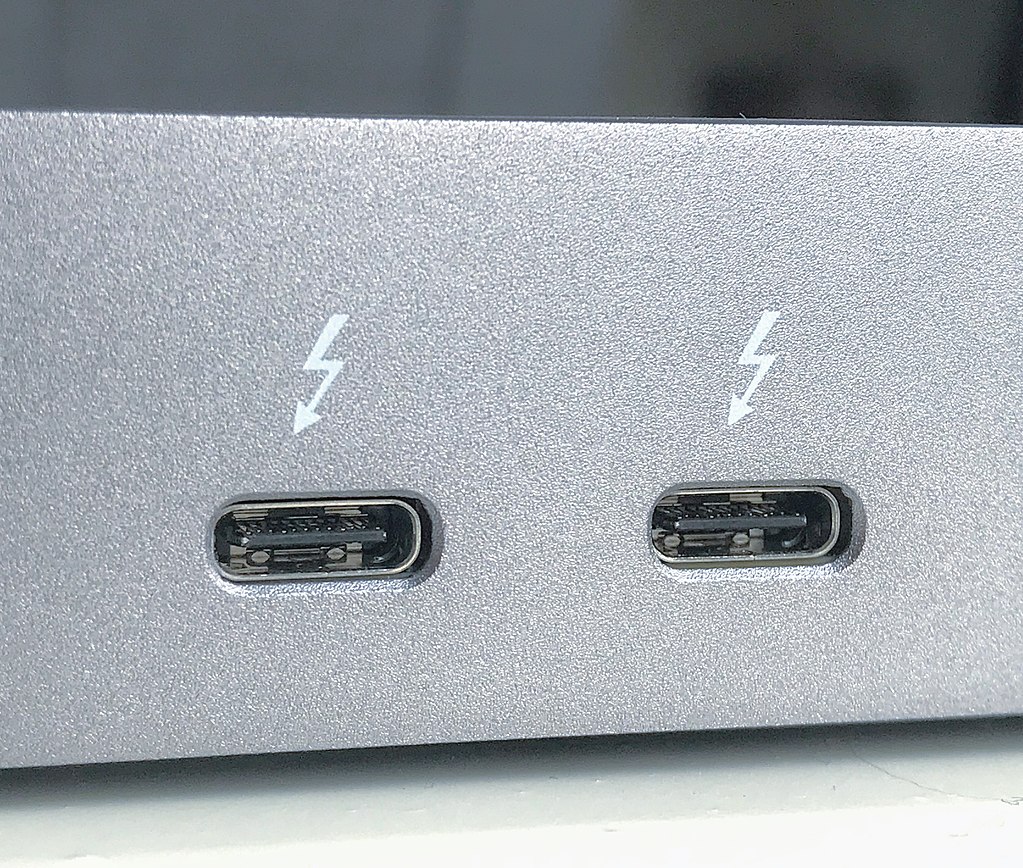
How to Identify a Thunderbolt 3 Port?
It is actually pretty easy to identify, generally, there is a small lightning bolt logo printed near the Type-C port. This means that the port supports Thunderbolt 3 but that doesn’t mean that the Type-C port only supports Thunderbolt. You can connect any Type-C device to it. Even a normal USB Type-A plug can be used on that Type-C port with a Type-C to Type-A converter.

In case you don’t know, Thunderbolt 3 is currently the latest and commonly used interface which offers 40Gb/s of data transfer rate. Thunderbolt 3 also can provide video data to the displays while serially supplying data to other devices like SSDs, hard drives, etc. thanks to its amazing feature called daisy-chaining.
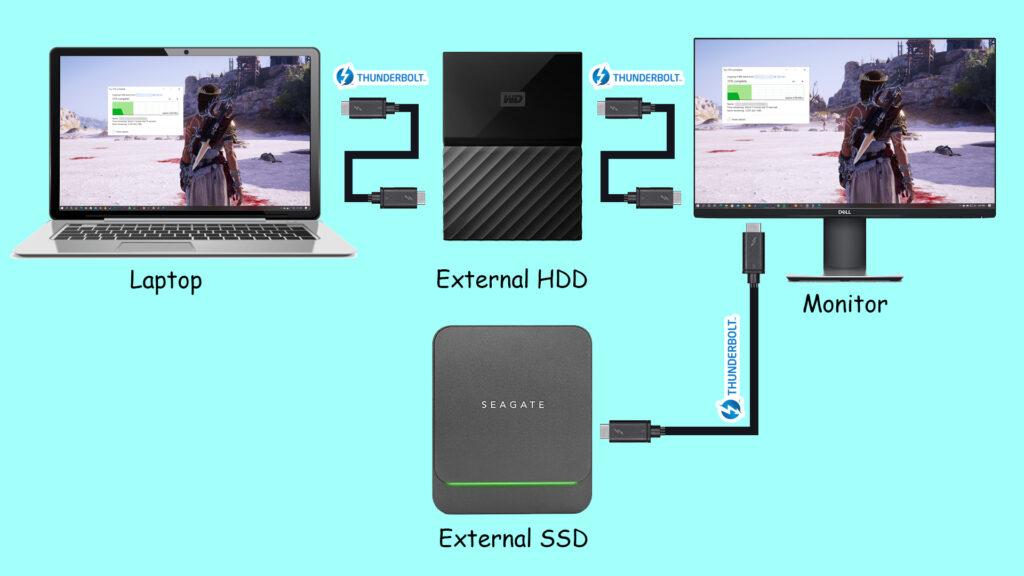

All Thunderbolt 3 controllers basically support “Thunderbolt Alternate Mode” and “DisplayPort Alternate Mode” because Thunderbolt can encapsulate DisplayPort data. Every Thunderbolt controller can either output DisplayPort signals directly over “DisplayPort Alternative Mode” or encapsulated within Thunderbolt in “Thunderbolt Alternate Mode”. Low-cost peripherals mostly connect via “DisplayPort Alternate Mode” while some docking stations tunnel DisplayPort over Thunderbolt.
Read Now: What is Thunderbolt? Versions & Features Explained
Bottom Line…
This is a pretty short description of USB Type-C. There is much more to tell which will be discussed later in a separate article. Hope you guys have enjoyed this article if so then don’t forget to comment down below. Thanks for visiting.

